you have first setup Windows Server 2008 and configured it for Active Directory, with DHCP. If you want to deploy operating systems within SCCM you will then also need the Windows Deployment Services installed.
You must have installed and configured IIS (for SCCM) and installed SQL Server 2005 SP2 (or SQL Server 2008 with this hotfix) and WSUS (you can install WSUS later if you want, it's only required for the SUP role).
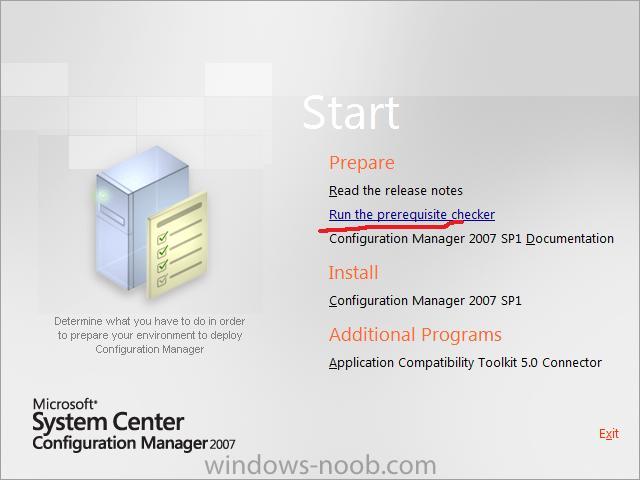
Run the prerequisite checker and fix the warnings/errors.
When the menu appears, click on Run the prerequisite checker, we'll do this to see if our Windows Server 2008 needs any additional tasks performed prior to installing SCCM 2007 sp1.
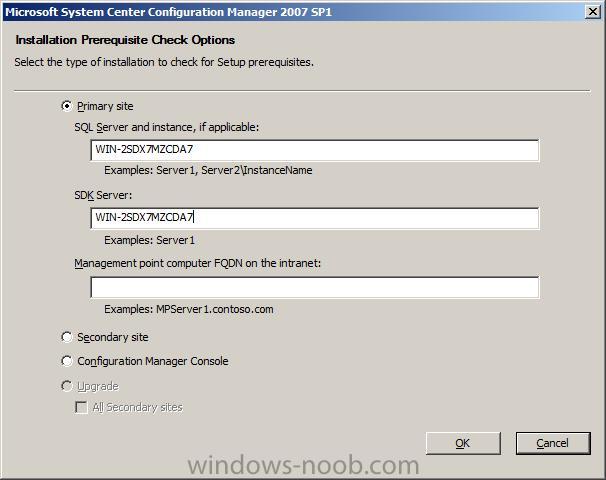
enter your servername as below (leave OUT the instance name or you may get errors explained in the Final Note)
this gave me two prerequisites which needed looking at, the AD Schema extensions, Microsoft Remote Differential compression.
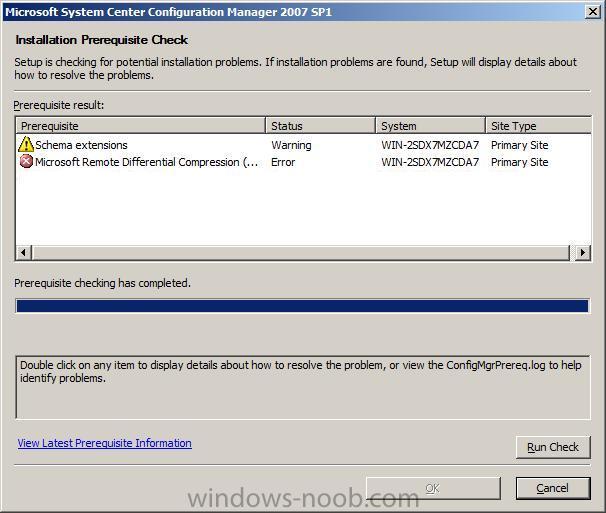
If you want to get more details of the problems identified, then check c:\ConfigMgrPrereq.log (and c:\ConfigMgrSetup.log) or double click each warning/error in turn to get a short description (scrollable) of the problem.
My first problem was that I needed to extend the Active directory schema, to do so I followed this guide.
Once I had extended the active directory schema, I ran the prerequisite checker again,
That left me with the RDC error,
That led me here and that in turn had this info
To add Remote Differential Compression to site servers and branch distribution points
In Server Manager, on the Features node, start the Add Features Wizard.
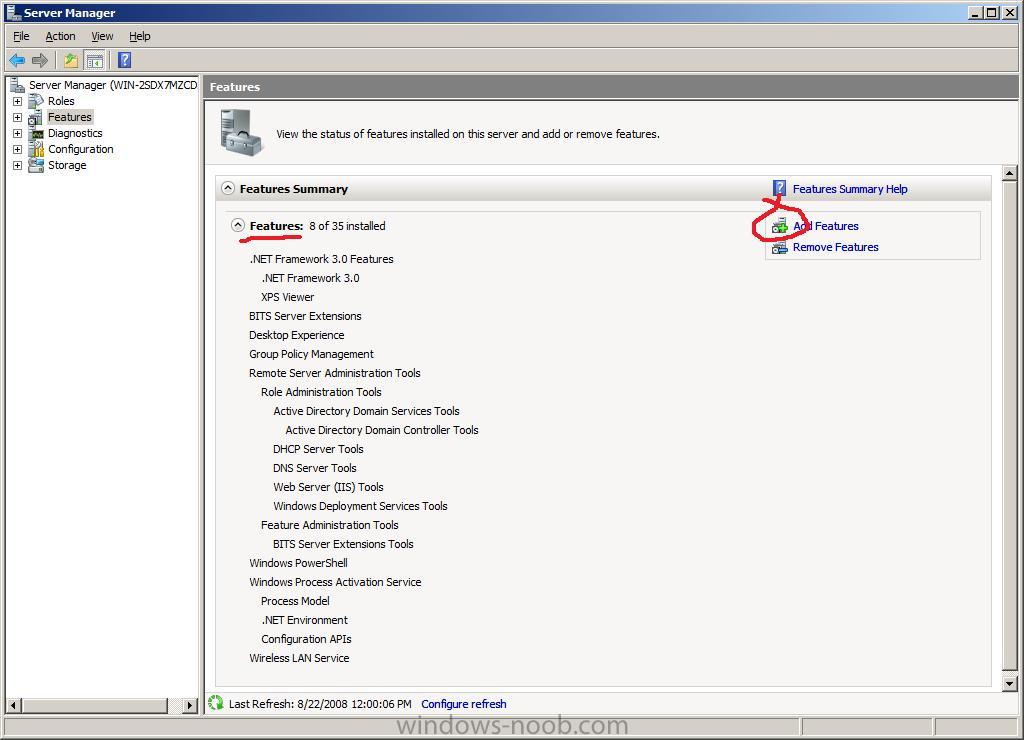
On the Select Features page, select Remote Differential Compression, and then click Next.
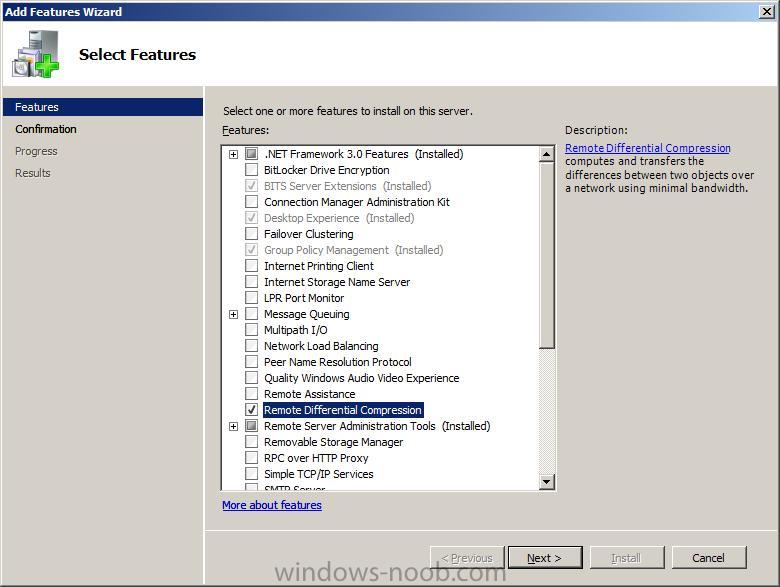
Complete the rest of the wizard by clicking install then close.
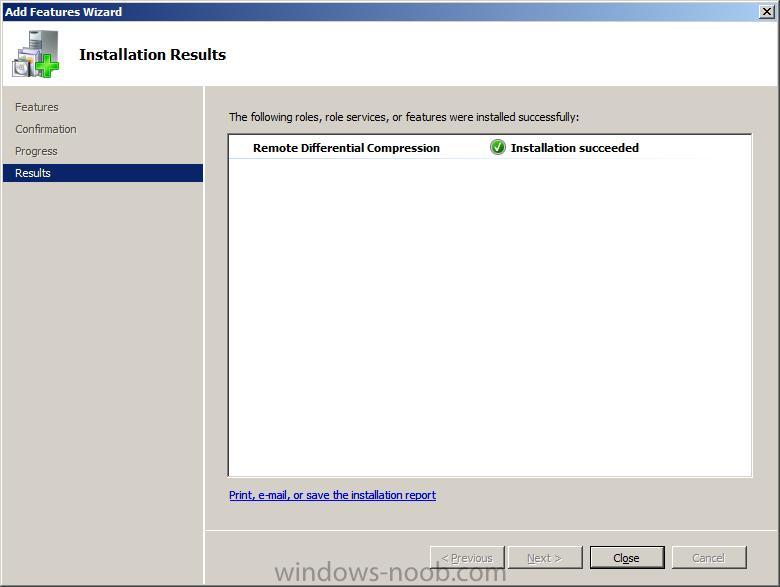
Now run the prerequisite checker again and the RDC error should be gone
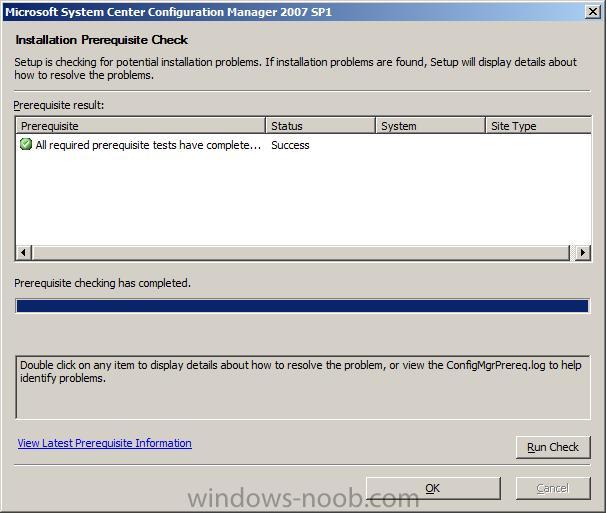
Once you have no warnings or errors, please proceed to Part 2.
Final Note: if you entered the instance name at the start of this guide, you may get an error which states
The Technet page for Setup Prerequisite checks states:-
Start the SCCM 2007 SP1 DVD and click on Configuration Manager 2007 SP1 under Install
review the welcome screen
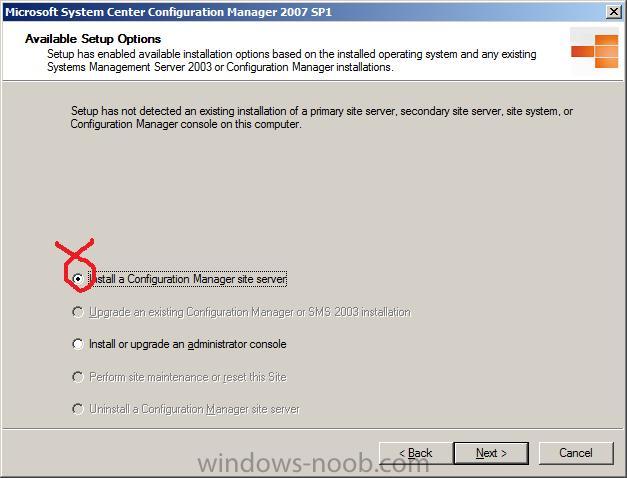
Choose the first option, Install a Configuration Manager site server
accept the license...
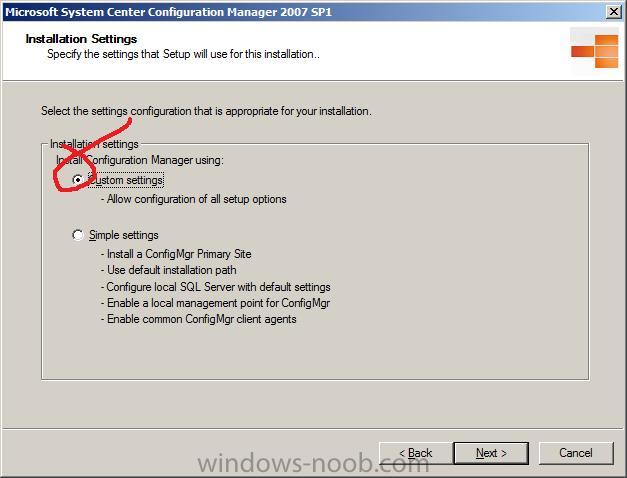
Next we get to choose the type of installation, as we want to see all the options, choose Custom
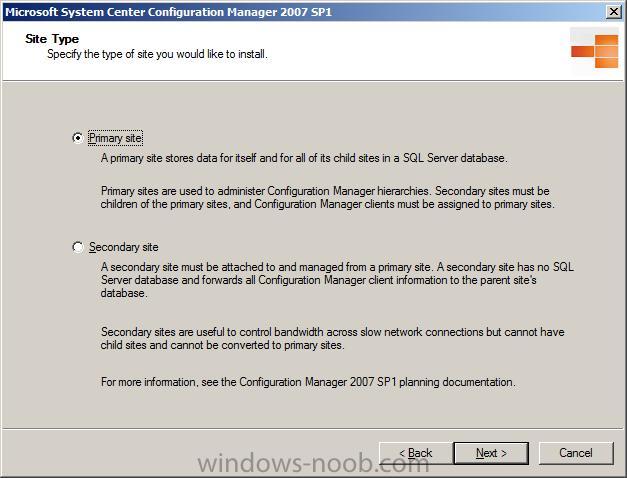
For Site Type, stick with the default (primary site)
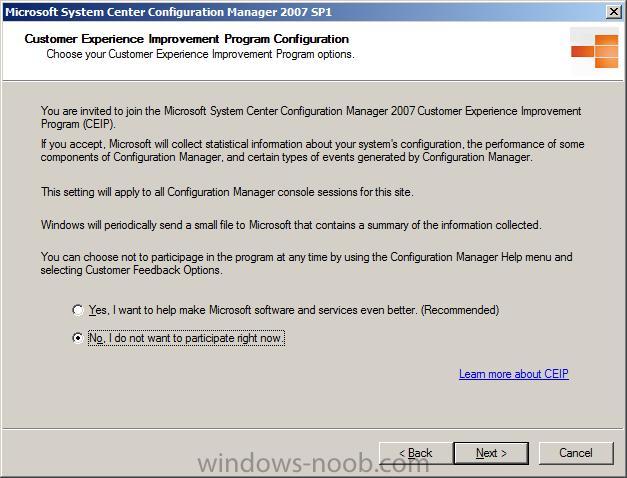
decide if you want to participate in CEIP
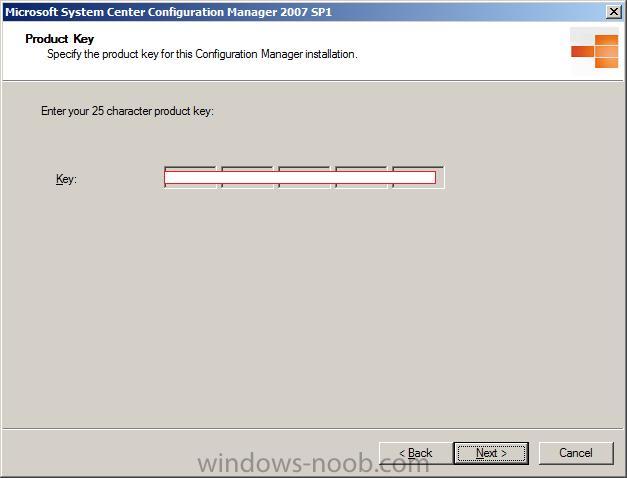
Specify your key
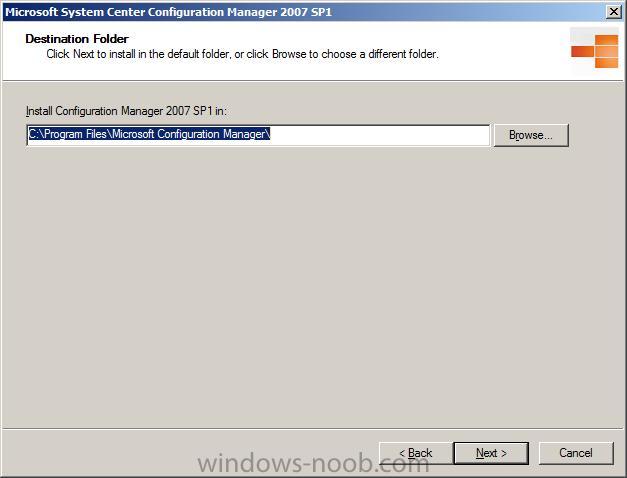
where to install it
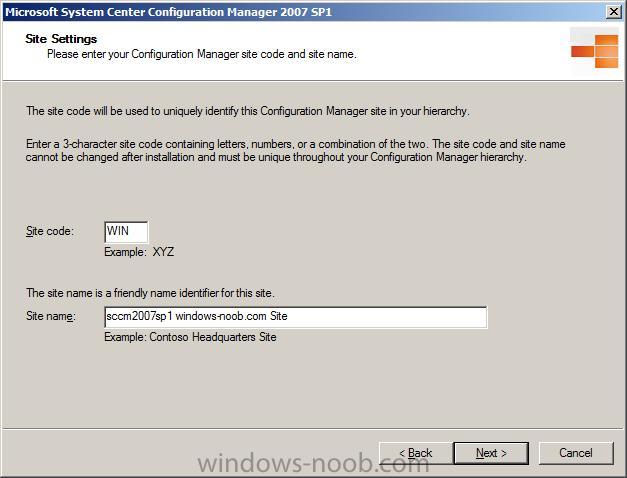
enter your Site Settings and Site Code name
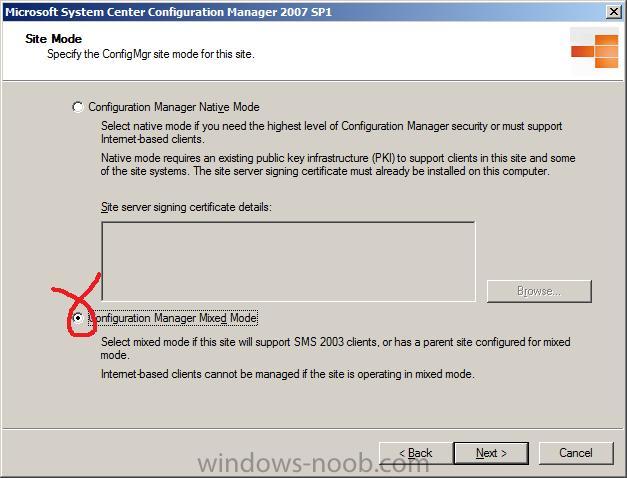
For the mode type, choose mixed mode (it is easier to setup and we can always migrate to Native mode in the future).
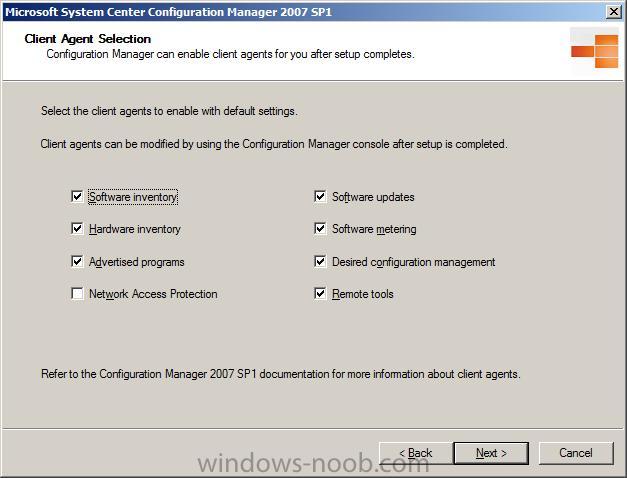
specify your client agent settings...
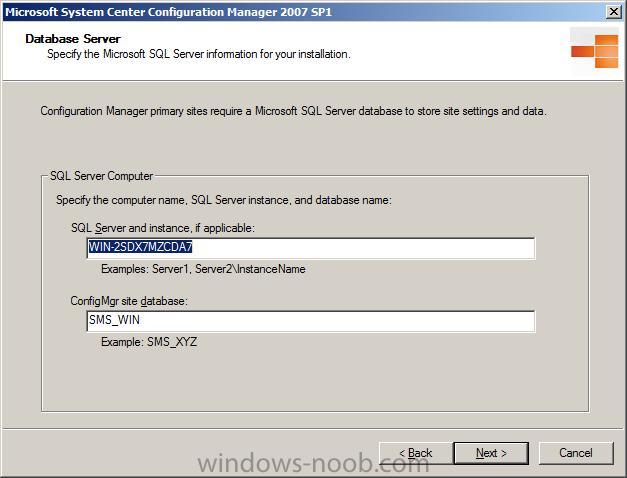
enter your Database server details
specify your SMS provider settings
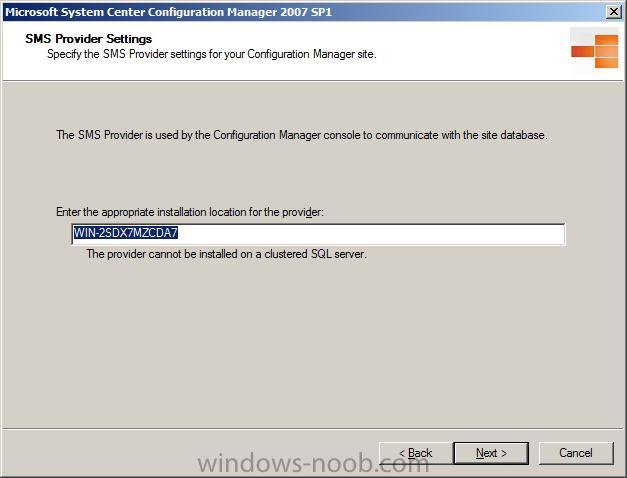
Note: The SMS Provider can be installed on the site database server computer, site server computer, or another server class computer (during setup at this point). The SMS Provider is used by the Configuration Manager console, Resource Explorer, tools and custom scripts used by Configuration Manager Admins to access site information stored in the site database.
specify the management point

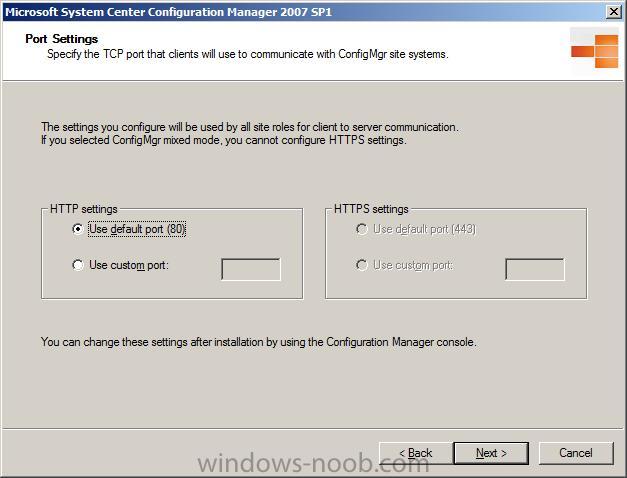
decide your TCP port settings
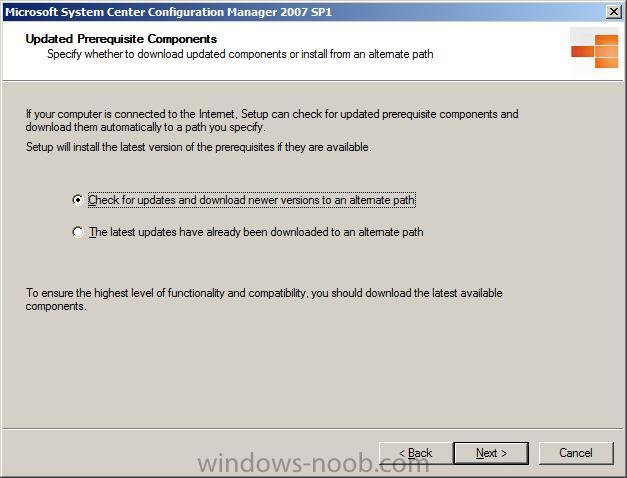
check for updates
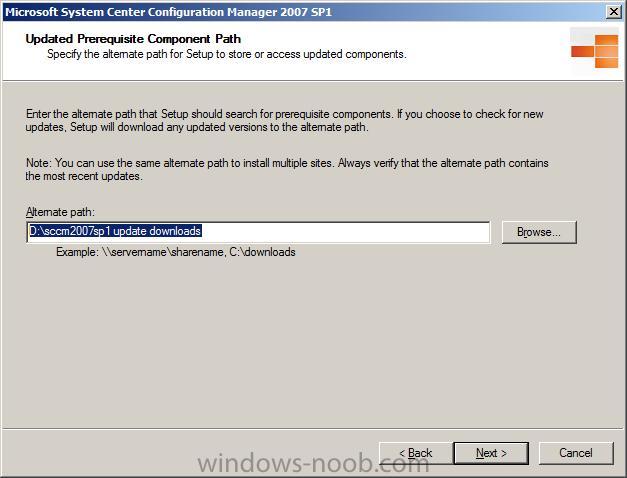
create a local folder to store these updates if necessary
updates will be downloaded...
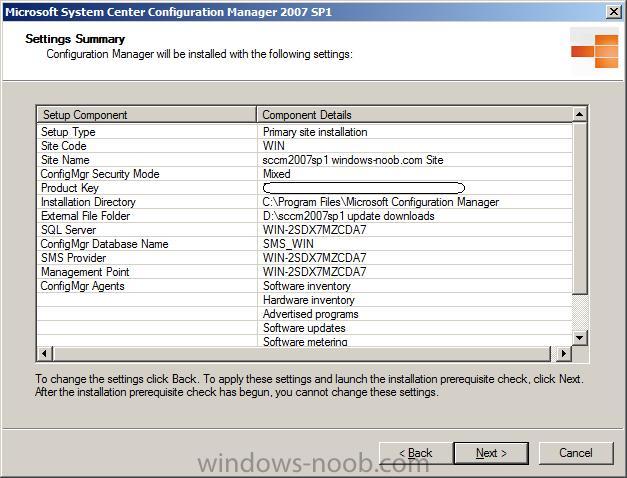
once done, click ok to review your settings summary
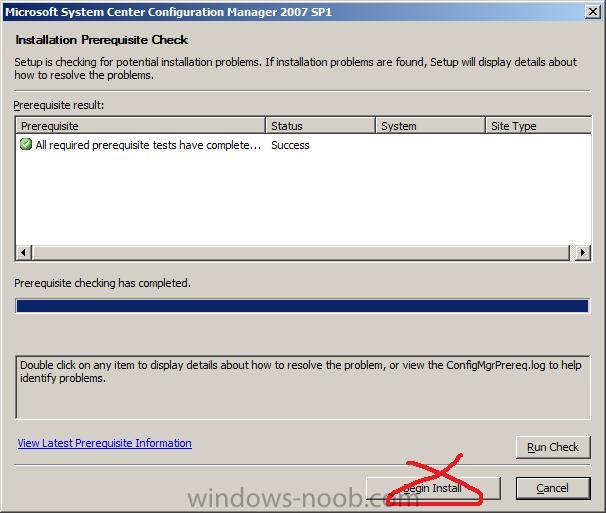
and click Next to start the prerequisite check (final)
as everything is ok, you can click on Begin Install
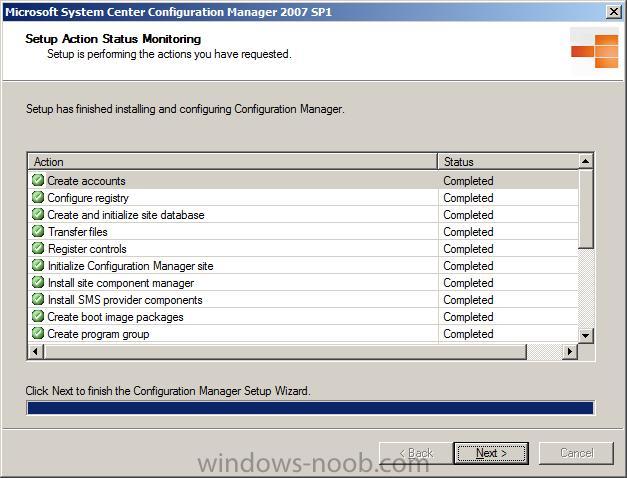
After a long wait you should see this
lets launch the configuration manager after closing
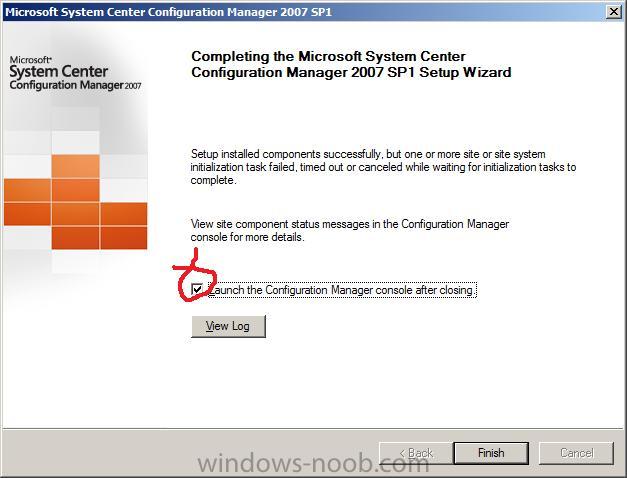
and click on Finish to finish the installation.
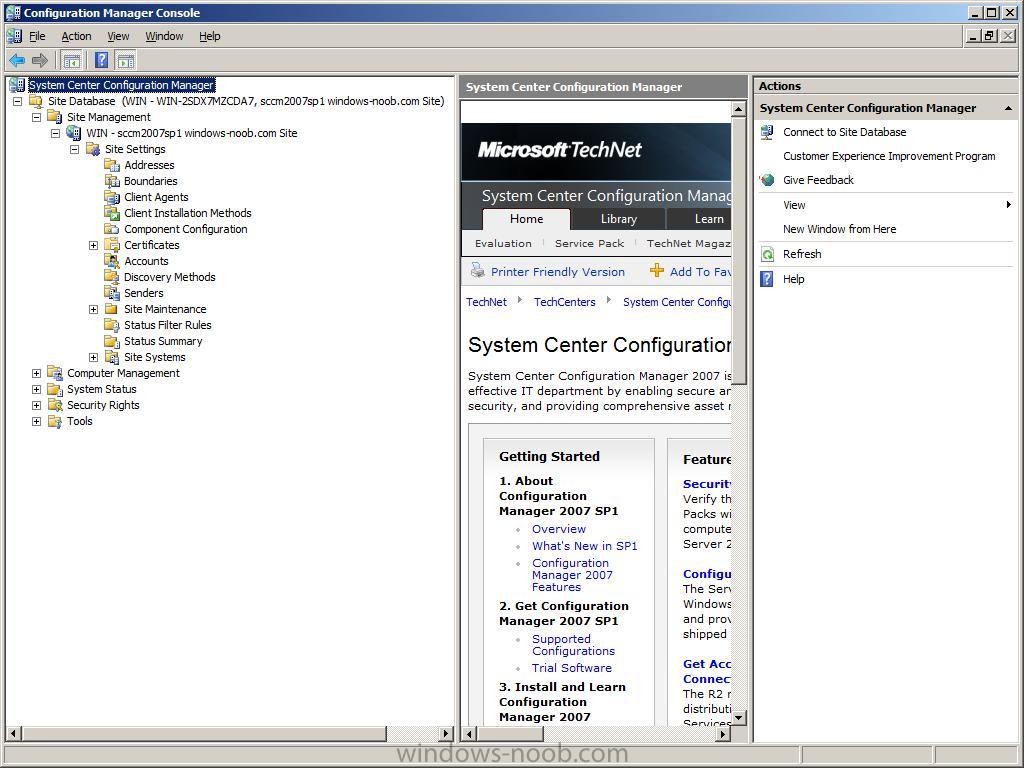
Congratulations, SCCM 2007 SP1 is now installed !
Note: At this point REBOOT your server.
You must have installed and configured IIS (for SCCM) and installed SQL Server 2005 SP2 (or SQL Server 2008 with this hotfix) and WSUS (you can install WSUS later if you want, it's only required for the SUP role).
Run the prerequisite checker and fix the warnings/errors.
When the menu appears, click on Run the prerequisite checker, we'll do this to see if our Windows Server 2008 needs any additional tasks performed prior to installing SCCM 2007 sp1.

enter your servername as below (leave OUT the instance name or you may get errors explained in the Final Note)

this gave me two prerequisites which needed looking at, the AD Schema extensions, Microsoft Remote Differential compression.

If you want to get more details of the problems identified, then check c:\ConfigMgrPrereq.log (and c:\ConfigMgrSetup.log) or double click each warning/error in turn to get a short description (scrollable) of the problem.
Quote
<08-22-2008 10:33:16> WIN-2SDX7MZCDA7; Schema extensions; Warning; Configuration Manager Active Directory schema extensions are not required, for site server installation, but are recommended to fully support the use of all Configuration Manager features.
My first problem was that I needed to extend the Active directory schema, to do so I followed this guide.
Once I had extended the active directory schema, I ran the prerequisite checker again,
That left me with the RDC error,
Quote
The Microsoft Remote Differential Compression (RDC) library must be registered for Configuration Manager site server installation
That led me here and that in turn had this info
Quote
Site servers and branch distribution points require Remote Differential Compression (RDC) to generate package signatures and perform signature comparison. RDC is not installed by default on computers running Windows Server 2008 and is not installed automatically during Configuration Manager Setup. For information about installing RDC on Windows Server 2008 computers, see How to Configure Windows Server 2008 for Site System Roles.
Site servers and branch distribution points require Remote Differential Compression (RDC) to generate package signatures and perform signature comparison. RDC is not installed by default on computers running Windows Server 2008.
To add Remote Differential Compression to site servers and branch distribution points
In Server Manager, on the Features node, start the Add Features Wizard.

On the Select Features page, select Remote Differential Compression, and then click Next.

Complete the rest of the wizard by clicking install then close.

Now run the prerequisite checker again and the RDC error should be gone

Once you have no warnings or errors, please proceed to Part 2.
Final Note: if you entered the instance name at the start of this guide, you may get an error which states
Quote
Either the user account running Configuration Manager Setup does not have sysadmin SQL Server role permissions on the SQL Server instance targeted for site database installation or the SQL Server instance could not be contacted to verify permissions. Setup cannot continue.
The Technet page for Setup Prerequisite checks states:-
Quote
Part 2. Install it !A SQL Server best practice is to remove the Builtin\Administrators group from the sysadmin role on installed SQL Server instances. If the Builtin\Administrators group has been removed from the sysadmin role, the user account running Configuration Manager Setup must be granted sysadmin role permissions for setup to succeed.
Start the SCCM 2007 SP1 DVD and click on Configuration Manager 2007 SP1 under Install

review the welcome screen

Choose the first option, Install a Configuration Manager site server

accept the license...

Next we get to choose the type of installation, as we want to see all the options, choose Custom

For Site Type, stick with the default (primary site)

decide if you want to participate in CEIP

Specify your key

where to install it

enter your Site Settings and Site Code name

For the mode type, choose mixed mode (it is easier to setup and we can always migrate to Native mode in the future).

specify your client agent settings...

enter your Database server details

specify your SMS provider settings

Note: The SMS Provider can be installed on the site database server computer, site server computer, or another server class computer (during setup at this point). The SMS Provider is used by the Configuration Manager console, Resource Explorer, tools and custom scripts used by Configuration Manager Admins to access site information stored in the site database.
specify the management point

decide your TCP port settings

check for updates

create a local folder to store these updates if necessary

updates will be downloaded...

once done, click ok to review your settings summary

and click Next to start the prerequisite check (final)
as everything is ok, you can click on Begin Install

After a long wait you should see this

lets launch the configuration manager after closing

and click on Finish to finish the installation.
Congratulations, SCCM 2007 SP1 is now installed !
Note: At this point REBOOT your server.

 Important
Important














